Drone User Basics
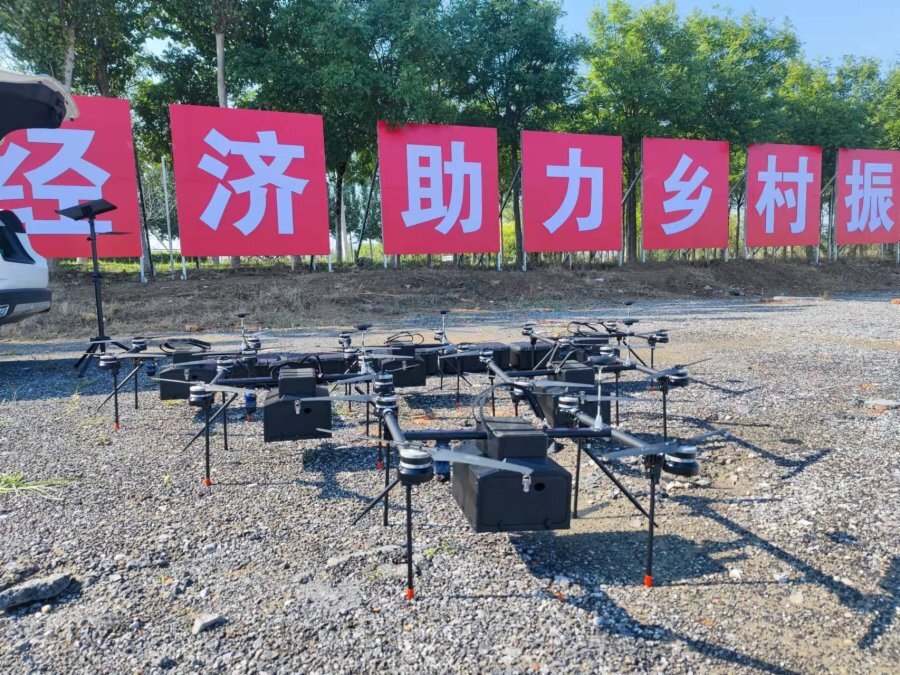

The Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Industry
The Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Industry
The unmanned aerial vehicle industry is exploding globally, driven by several major operations such as construction and disaster relief. While the military sector is already a key driver of the market, the commercial sector will continue to grow rapidly in the coming years due to the rapid adoption of the technology in agricultural, forest, and crop monitoring. Other major applications for the unmanned aerial vehicle are in the transportation and logistics industries, where companies such as Uber have invested heavily in new air taxi services.
The military has long led the way in the use of unmanned aerial vehicles, but only recently have civilians become able to fly them. Until now, this technology has only been available to the military, and remained limited to the hobby of flying radio controlled model aircraft. As such, it is essential to develop a comprehensive understanding of these emerging technologies and how they can benefit our nation. And to that end, we must first understand the nature of these new systems and how to detect them.
One of the most impressive applications of drone technology is in disaster relief. These unmanned aircraft can gather huge amounts of accurate data, and they can even take excellent aerial photographs and videos. The data collected by drones can then be transformed into 3D maps and models - especially important in disaster areas. Drones that are equipped with high-resolution cameras are also popular in live streaming. They can be used to monitor the health of disaster victims and help them rebuild their homes.
There are many other uses for unmanned aerial vehicles, and the first use was as a training tool. The military used drones as targets in training, and many countries began using them after World War II. But, in the early 1980s, a new generation of unmanned aircraft was developed. The Israeli Air Force developed the tactical UAV and fitted small drones with infrared cameras and laser-guided munitions. The drones proved useful in combat, and the United States acquired early Israeli drones and produced them under license.
The technology has many applications, but it's important to understand the differences between these two types of aircraft. Most have a command and control link with an operator, and some have payloads that are lighter than a human. Military UAVs are generally much lighter than crewed versions. Depending on their intended use, the payload can be autonomous or active human control. They can be used to survey terrain or collect data.
0users like this.